As it giet om it mjitten en dosearjen fan in spesifyk folume fan in floeistof, binne pipetten ûnmisber yn 'e hjoeddeiske laboratoariumomjouwing. Ofhinklik fan 'e grutte fan it laboratoarium en it folume dat dosearre wurde moat, wurde ferskate soarten pipetten faak brûkt:
- Loftferpleatsingspipetten
- Positive ferpleatsingspipetten
- Dosearringspipetten
- Pipetten mei ferstelbere berik
Yn 2020 begjinne wy te sjen dat loftferpleatsingsmikropipetten in krúsjale rol spylje yn 'e striid tsjin COVID-19, en se wurde brûkt foar it tarieden fan stekproeven foar it opspoaren fan patogenen (bygelyks, real-time RT-PCR). Typysk kinne twa ferskillende ûntwerpen brûkt wurde, hânmjittige of motorisearre loftferpleatsingspipetten.
Manuele loftferpleatsingspipetten vs. motorisearre loftferpleatsingspipetten
Yn it foarbyld fan in loftferpleatsingspipet wurdt in piston omheech of omleech yn 'e pipet beweecht om negative of positive druk op 'e loftkolom te meitsjen. Hjirmei kin de brûker in floeibere stekproef ynademe of útstjitte mei in wegwerppipettip, wylst de loftkolom yn 'e tip de floeistof skiedt fan 'e net-wegwerpdielen fan 'e pipet.
De beweging fan 'e piston kin ûntwurpen wurde om mei de hân troch de operator of elektroanysk dien te wurden, d.w.s. de operator beweecht de piston mei in drukknop-kontroleare motor.
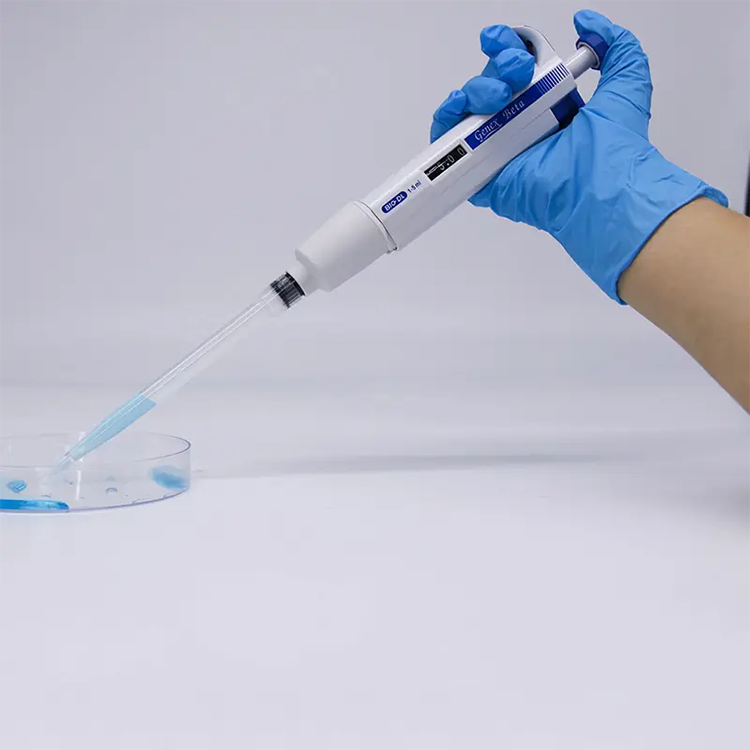

Beperkingen fan hânmjittige pipetten
Langduorjend gebrûk fan hânmjittige pipetten kin ûngemak en sels ferwûnings feroarsaakje by de operator. De krêft dy't nedich is om floeistoffen te dosearjen en de pipettepunt út te werpen, kombineare mei faak werhelle bewegingen oer ferskate oeren, kin de gewrichten, benammen de tomme, elleboog, pols en skouder, in RS-risiko (I repetitive muscle strain) fergrutsje.
Hânmjittige pipetten fereaskje dat de tommeknop yndrukt wurdt om de floeistof frij te litten, wylst elektroanyske pipetten bettere ergonomyen biede mei in elektroanysk aktivearre knop yn dit foarbyld.
Elektronyske alternativen
Elektroanyske of motorisearre pipetten binne ergonomyske alternativen foar hânmjittige pipetten dy't de sampleútfier effektyf ferbetterje en presyzje en krektens garandearje. Oars as tradisjonele tomme-kontroleare knoppen en hânmjittige folume-oanpassingen, komme elektryske pipetten mei in digitale ynterface om folume oan te passen en te aspirearjen en te ûntladen fia in elektrysk oandreaune piston.
Motorseleksje foar elektroanyske pipetten
Omdat pipetterjen faak de earste stap is yn in proses mei meardere stappen, kinne alle ûnkrektens of ûnfolsleinheden dy't foarkomme by it mjitten fan dit lytse diel floeistof troch it heule proses field wurde, wat úteinlik ynfloed hat op de algemiene krektens en presyzje.
Wat is krektens en presyzje?
Krektens wurdt berikt as in pipette itselde folume meardere kearen útjout. Krektens wurdt berikt as de pipette it doelfolume sekuer sûnder flaters útjout. Presyzje en krektens binne lestich tagelyk te berikken, mar de yndustryen dy't pipetten brûke fereaskje sawol presyzje as krektens. Eins is it dizze kritysk hege standert dy't it mooglik makket om eksperimintele resultaten te reprodusearjen.
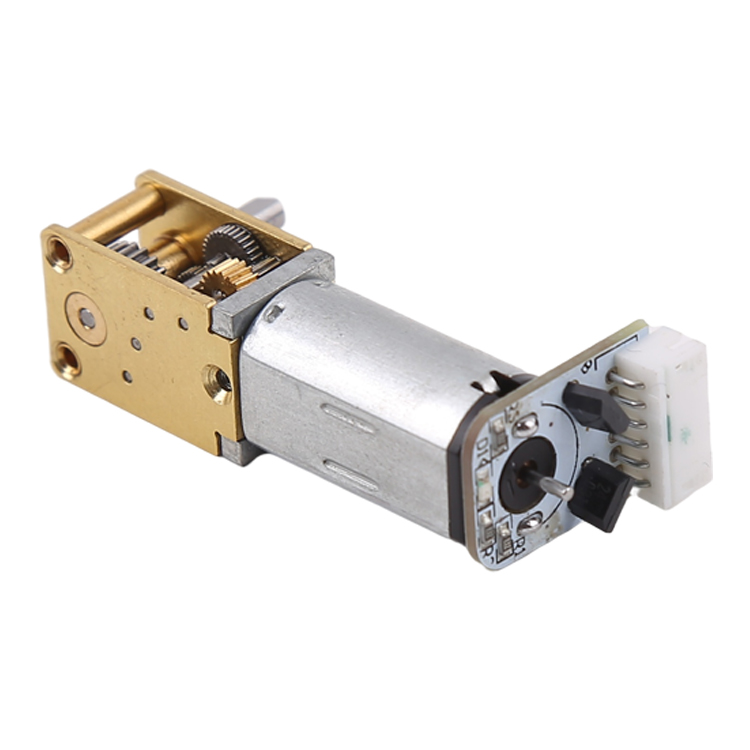
It hert fan elke elektroanyske pipette is de motor, dy't de presyzje en krektens fan 'e pipette signifikant beynfloedet, neist in oantal oare wichtige faktoaren lykas pakketgrutte, krêft en gewicht. Pipetûntwerpingenieurs kieze primêr foar stapmotors of DC-motors. Sawol stapmotors as DC-motors hawwe lykwols har eigen foar- en neidielen.
DC-motors
DC-motors binne ienfâldige motors dy't draaie as der gelijkstroom oanlein wurdt. Se hawwe gjin yngewikkelde ferbiningen nedich om de motor te draaien. Mei it each op de lineêre bewegingseasken fan elektroanyske pipetten, hawwe DC-motoroplossingen lykwols in ekstra leadskroef en fersnellingsbak nedich om de rotearjende beweging yn lineêre beweging om te setten en de fereaske krêft te leverjen. DC-oplossingen fereaskje ek in feedbackmeganisme yn 'e foarm fan in optyske sensor of encoder om de posysje fan 'e lineêre piston sekuer te kontrolearjen. Fanwegen de hege traachheid fan syn rotor kinne guon ûntwerpers ek in remsysteem tafoegje om de posysjonearringskrektens te ferbetterjen.

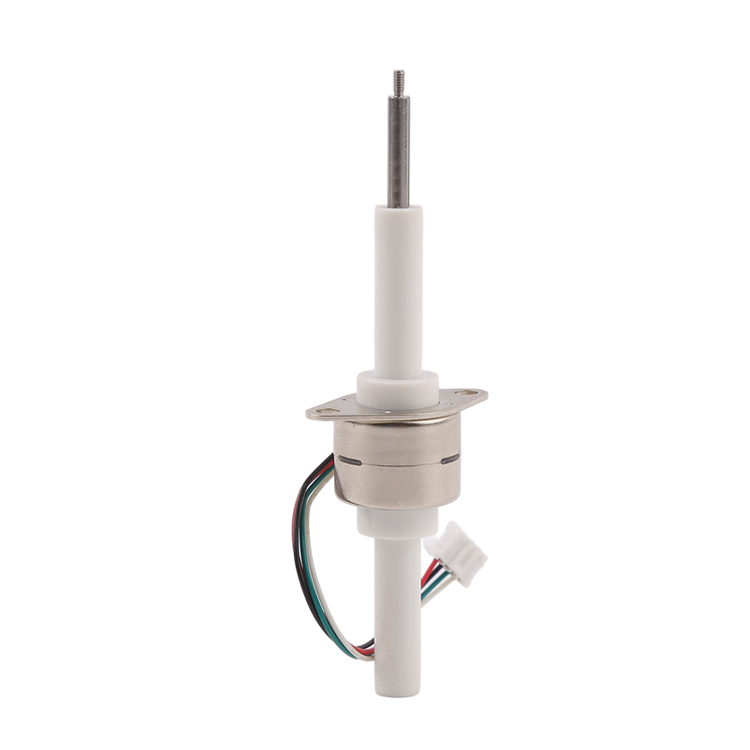
Stapmotors
Oan 'e oare kant hawwe in protte yngenieurs in foarkar foar lineêre aktuatoroplossingen mei stappenmotors fanwegen har gemak fan yntegraasje, poerbêste prestaasjes en lege kosten. Lineêre aktuators mei stappenmotors mei permaninte magneet mei in skroefdraadrotor en in yntegreare filamentbalke om direkte lineêre beweging yn lytse pakketten te produsearjen.

Pleatsingstiid: 19 juny 2024
